are suppliers internal or external swot analysis ,when to use swot analysis,are suppliers internal or external swot analysis, SWOT Analysis (also known as SWOT Matrix) is a business framework that helps assessing a wide variety of factors that may have a . $38.00
SWOT analysis is a widely used tool for strategic planning, allowing organizations to evaluate their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. When analyzing a company’s strategic position, a key question often arises: Are suppliers considered part of the internal or external elements in a SWOT analysis? To answer this question, it is essential to explore the relationship between suppliers and a business, considering both the internal and external factors that influence an organization’s operations.
In this article, we will examine the role of suppliers in the SWOT framework, provide an overview of the concepts of internal and external analyses, and clarify when suppliers are considered internal or external factors in SWOT analysis. Furthermore, we will explore how Porter's Five Forces, a complementary strategic tool, interacts with SWOT to offer a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s competitive environment.
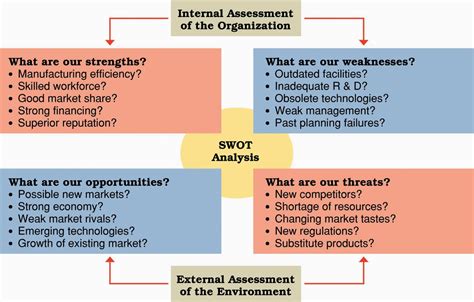
What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a strategic tool used by businesses to identify their internal and external factors that could affect their ability to achieve their goals. The framework is divided into four key categories:
1. Strengths (Internal): These are the positive internal attributes or resources that an organization possesses. Examples include a strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, or proprietary technology.
2. Weaknesses (Internal): These are internal factors that limit the organization's ability to achieve its objectives. Examples include high employee turnover, lack of resources, or outdated technology.
3. Opportunities (External): These are factors in the external environment that the organization could leverage to its advantage. Examples include emerging markets, technological advancements, or regulatory changes.
4. Threats (External): These are external factors that could potentially harm the organization. Examples include economic downturns, increased competition, or changes in consumer preferences.
Internal vs. External in SWOT Analysis
Before delving into the specific role of suppliers, it is important to understand the distinction between internal and external factors in SWOT analysis:
- Internal Factors refer to aspects that are within the control of the organization, such as management decisions, company culture, operational efficiency, and internal resources.
- External Factors are elements that exist outside of the organization and are typically beyond its direct control. These include the broader industry environment, competitors, economic conditions, and relationships with suppliers and customers.
The classification of factors as internal or external is critical because it helps businesses prioritize actions. Internal factors typically require changes within the organization itself, while external factors often require businesses to adapt or respond to external conditions.
Suppliers in the Context of SWOT Analysis
The role of suppliers in a SWOT analysis is primarily considered an external factor, but this can be nuanced depending on how the relationship is managed. Let’s explore the arguments for both perspectives.
# Suppliers as an External Factor
In most cases, suppliers are classified as external factors in a SWOT analysis because they exist outside the organization. Here are some reasons why suppliers are typically considered external:
1. Control and Influence: While companies may build strong relationships with suppliers, they do not have direct control over their suppliers’ business decisions. Suppliers make independent decisions about pricing, quality, and delivery terms, which can influence the buyer’s strategic position but are largely beyond the company’s direct influence.
2. Competitive Environment: Suppliers are part of the broader competitive landscape that companies must navigate. According to Porter’s Five Forces framework, the bargaining power of suppliers is one of the key forces that determine the level of competition and profitability within an industry. If suppliers have strong bargaining power (e.g., they are few in number or provide a unique product), they can pose a threat to businesses by increasing costs or reducing product quality.
3. External Opportunities and Threats: Suppliers create both opportunities and threats from an external perspective. A reliable, cost-effective supplier can be a valuable opportunity for a company to improve its efficiency and profitability. Conversely, a supplier who fails to meet quality standards, delivers late, or increases prices could pose a significant threat to the business.
4. Industry-Specific Factors: In some industries, such as manufacturing or retail, suppliers play a critical role in the supply chain. Companies that rely heavily on raw materials, parts, or services from suppliers may find that their relationships with suppliers are critical to maintaining competitiveness. However, even in such cases, suppliers are considered external entities that may influence the business from the outside.
# Suppliers as an Internal Factor

are suppliers internal or external swot analysis The sticker, Chanel logo, and hologram design varied with the manufacturing date (see chart below). Note that over time, serial number stickers may become detached from handbags. .
are suppliers internal or external swot analysis - when to use swot analysis